Understanding e-invoicing
E-invoicing is in reference to invoices that are issued, received and processed electronically –essentially, they are digital throughout their lifecycle. The Accounts Payable Association defines e-invoicing as a ‘structured, tax compliant, authenticated invoice data issued from a supplier to a buyer.’
Structured data enables the accurate and compliant transfer of invoices. By sending an invoice in data form, through EDI or XML, human interference isn’t required to understand the content of the invoices. Teams no longer have to manually assess information sent via unstructured data, like PDF documents, instead, it passes through an organisation’s IT systems.
How it works
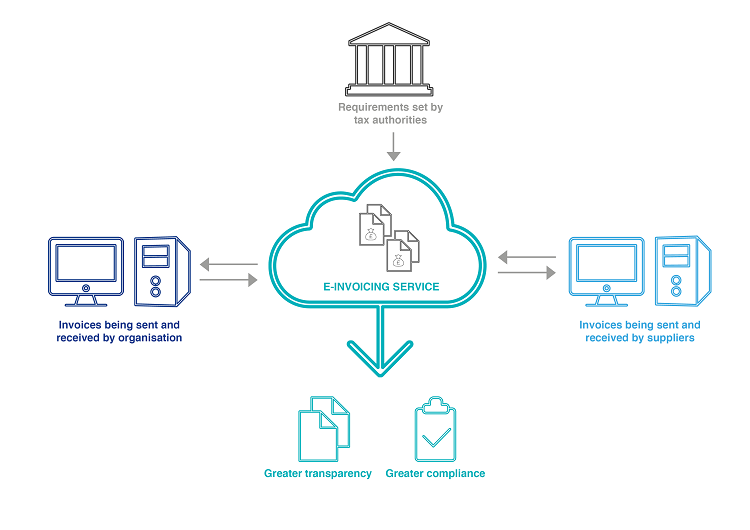
The importance of technology platforms
Technology platforms play an important role in ensuring effective e-invoicing. IT systems can be programmed to read and understand purchase order codes, goods received and digital signatures, among other elements. Bespoke, country-specific business rules can also be applied, ensuring invoices are compliant with processes, while flagging those that aren’t. These rules and programmes remain flexible to incorporate changes to legislation. By integrating e-invoicing with internal IT systems, invoices are understood, analysed and processed accurately, without misinterpretation. The same process applies for issuing invoices; it becomes an automated process.
Countries implementing e-invoicing benefit from a real-time view of all data produced and received, providing full transparency and greater oversight of economic activity. This information empowers policy makers to make data-driven policy decisions that focus on helping underperforming sectors that need more support.
The roadmap to e-invoicing
Across the world, businesses supply, or work with, public sector and governmental bodies on a daily basis. Introducing e-invoicing allows countries to streamline their ability to process data and, more importantly, implement tax laws and requirements. By setting a standardised invoicing requirement, businesses have to comply to complete the work. For example, in 2014, the European Union (EU) introduced the eInvoicing Directive 2014/55/EU; a standard to streamline the varied and complex e-invoicing processes used by EU member states. The directive set a data model outlining all relevant information required for e-invoicing.
Before an e-invoicing system can be rolled out, there must be a drive to change and be more compliant. In November 2020, Egypt introduced mandatory e-invoicing. According to Egypt’s Minister of Finance, the drive to transform the existing billing system was an important part of the country’s digital transformation. The new system allows instant data exchange and validation, and proactively targets ‘Egypt’s black market and informal economy.’
Once the intention is made, the focus is on ensuring the right legislation, rules and processes are in place, as they form the base of any good e-invoicing system. Following this, authorities need the appropriate technology platforms to meet e-invoicing requirements. In Russia, for example, where e-invoicing was normalised in 2017, invoices must be produced in XML as a UTD format set by the Federal Tax Service. Invoices are submitted for a local digital signature via encryption software, which is only provided by certified Russian software providers.
A user-friendly, automated e-invoicing system is of great benefit to all stakeholders; from the country implementing it to the governmental body managing it, and the taxpayers, supply chain partners and businesses utilising it. The entire process is compliant and in strict accordance with country-specific tax laws and legislation.
The benefits of e-invoicing
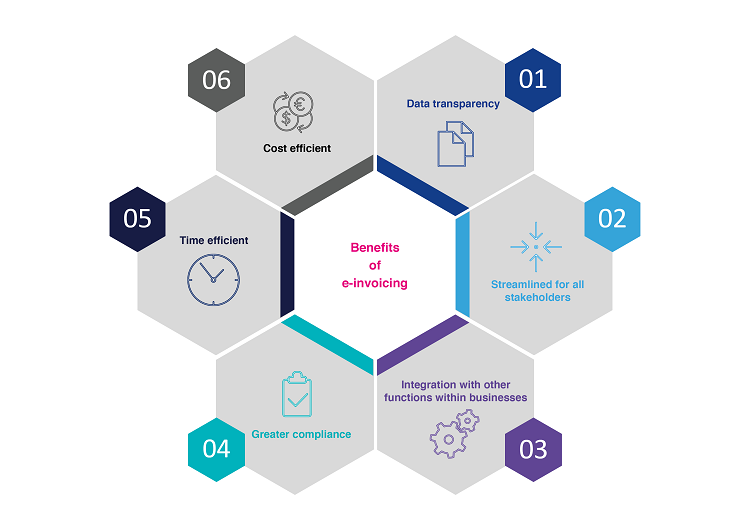
Conclusion
As more countries transform traditional ways of working, e-invoicing is an important part of their digital journey. Managing payments and billing is the backbone of operating an efficient business, and to deliver a holistic e-invoicing system, technology must work in cohesion with business rules. Inefficient and time-consuming invoicing practices are replaced with streamlined, data-driven processes that empower the countries implementing them, as well as the communities they support.


